A) amino acid.
B) dipeptide.
C) tripeptide.
D) polypeptide.
E) protein.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the strategy used for treating hypertension through drug therapies?
A) The strategy is to suppress how the body detects sodium.
B) The strategy is to suppress how the body detects low blood pressure.
C) The strategy is to lower blood pressure directly.
D) The strategy is to permanently disable renin.
E) The strategy is to inhibit the pathway that the body uses to increase blood pressure.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Hydrolysis of the peptide bonds in peptide below would result in 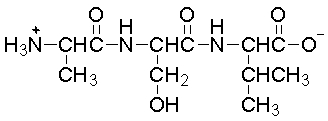
A) no reaction.
B) a single amino acid.
C) two amino acids.
D) three amino acids.
E) four amino acids.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which side chain would most likely be found in the interior of a protein, away from the aqueous environment?
A) -CH2OH
B) -CH2SH
C) -CH2COOH
D) -CH2CONH2
E) ![]()
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When several amino acids are connected together, head-to-tail, the resulting molecule is called a(n) __________. When many amino acids are connected together, the molecule is called a(n) ___________.
A) enzyme; polypeptide
B) protein; polypeptide
C) polypeptide; protein
D) polypeptide; enzyme
E) nucleic acid; enzyme
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following amino acids is polar neutral? 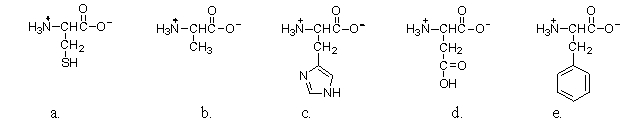
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about disulfide bridges is FALSE?
A) Disulfide bridges are found in the tertiary structure of a protein.
B) Disulfide bridges can occur between nonadjacent, and even distant, amino acids.
C) Disulfide bridges are covalent bonds.
D) Reducing a disulfide bridge gives two thiols.
E) A disulfide bridge is weaker than a hydrogen bond.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement best describes how an enzyme lowers the activation energy of a reaction?
A) The enzyme covalently binds to the substrate, lowering its energy.
B) The enzyme chemically reacts with the substrate to make it more reactive.
C) The enzyme increases the temperature of the substrate, making it more reactive.
D) The substrate is held in the correct orientation for reaction to occur.
E) All of the above
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does the potential energy of a correctly folded protein compare to the energy of an unfolded protein or a wrongly folded one?
A) The energy of a correctly folded protein is lower.
B) The energy of a correctly folded protein is higher.
C) The energy of proteins is the same no matter how they are folded or unfolded.
D) Proteins do not have energy.
E) Sometimes the energy of a correctly folded protein is lower and sometimes it is higher.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements best describes the induced-fit model of enzyme action?
A) In this model, the enzyme changes the shape of a substrate using a cofactor.
B) In this model, the enzyme adjusts it shape to adapt to the shape of the substrate.
C) In this model, the enzyme induces a change of polarity in the substrate that results in bonding.
D) In this model, the enzyme's active site is complementary to the shape of the substrate.
E) In this model, the enzyme's active site chemically reacts with the substrate.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The structure of one of the first ACE inhibitors is given below. What is the purpose of the sulfur in this molecule? 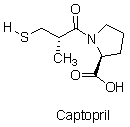
A) It is highly reactive with angiotensin II.
B) It binds to a metal on the exterior of ACE.
C) It holds the molecule in the active site of ACE.
D) It makes Captopril into a strong acid.
E) It forms a covalent bond with ACE, permanently deactivating it.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Physiological pH is a pH of approximately
A) 5.7.
B) 7.3.
C) 8.1.
D) 9.1.
E) 0.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the amino acids in the following structure are at the N-terminus? 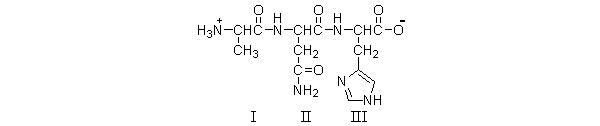
A) all of them
B) I only
C) III only
D) II and III
E) I and III
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is NOT one of the four categories of biomolecules?
A) proteins
B) vitamins
C) lipids
D) carbohydrates
E) nucleic acids
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a complete protein?
A) meat
B) milk
C) eggs
D) soy
E) All of these are complete proteins.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following correctly shows the electrostatic interaction between amino acids that holds an -helix or -pleated sheet together? 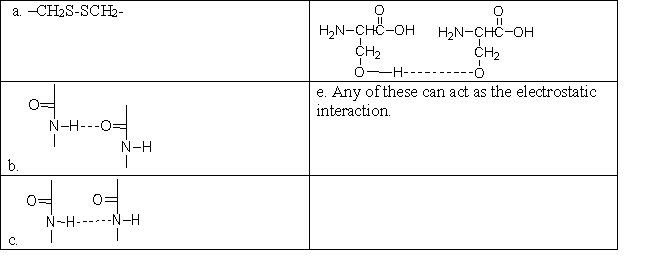
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures illustrates an amino acid in a solution with a high pH? 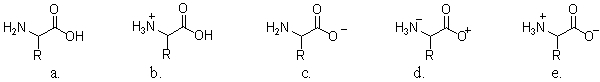
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following is a description of an enzyme called superoxide dismutase. Refer to this paragraph to answer the following question. Superoxide dismutase is an enzyme that detoxifies a free radical called superoxide. This radical is responsible for causing injury during reperfusion after a heart attack, and is also thought to play a role in Parkinson's Disease.a Depending on what organism the protein is found in, it occurs either as a dimer or tetramer of identical subunits.b The subunits are mostly -helical with some β-sheet near the C-terminus.c A metal binding site for manganese, iron, nickel or copper/zinc is composed of residues from both the N-terminus and the C-terminus.d These residues are: His-26, His-81, Asp-167, His-171.e Which statement refers to primary structure?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why doesn't denaturation affect the primary structure of a protein?
A) Actually, denaturation does hydrolyze amino acids.
B) because peptide bonds are higher energy bonds than other interactions
C) because peptide bonds are stronger than other interactions
D) because peptide bonds are weaker than other interactions
E) because peptide bonds cannot be broken under any circumstances
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the amino acids does NOT contain a chiral carbon? 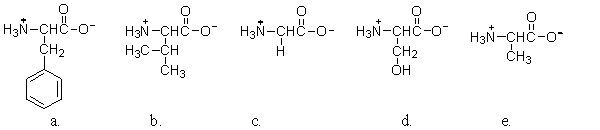
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 122
Related Exams