A) 1931; early 1970s
B) 1961; early 1970s
C) 1981; early 1990s
D) 1991; early 2000s
E) 1921; early 1980s
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the government implements expansionary fiscal policy that raises aggregate demand, but the policy is unanticipated. According to new classical theory, in the short run the price level would ____________ and Real GDP would ______________. In the long run, new classical theory would predict that the price level would ______________ compared to its original long-run equilibrium level and that Real GDP would ____________.
A) rise; decline; rise; remain unchanged
B) rise; rise; rise; remain unchanged
C) rise; decline; remain unchanged; rise
D) fall; rise; remain unchanged; rise
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy is initially in long-run equilibrium. Expectations are adaptive, prices and wages are flexible, and there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand. In the short run, the price level will be __________ than it was in long-run equilibrium and Real GDP will be __________ than it was in long-run equilibrium.
A) higher; lower
B) lower; higher
C) lower; lower
D) higher; higher
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy is in long-run equilibrium when there is a correctly anticipated increase in aggregate demand. In new Keynesian theory, the price level will rise __________ in the short run than it is predicted to rise in new classical theory.
A) by more
B) by less
C) by the same amount
D) faster
E) slower
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that the government implements expansionary fiscal policy that raises aggregate demand, but individuals incorrectly anticipate the policy measure (bias upward) . According to new classical theory, in the short run the price level would ____________ and Real GDP would ______________. In the long run, new classical theory would predict that the price level would ______________ compared to its original long-run equilibrium level and that Real GDP would _____________.
A) rise; decline; rise; remain unchanged
B) fall; rise; rise; remain unchanged
C) rise; decline; remain unchanged; rise
D) fall; rise; remain unchanged; rise
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One of the ideas that found a permanent place in macroeconomics after Milton Friedman's presidential address to the American Economic Association in 1967 was that
A) there is not only a temporary tradeoff between inflation and unemployment, but a permanent tradeoff as well.
B) the tradeoff between unemployment and inflation exists only in the long run, but not in the short run.
C) people's expectations about economic events affect economic outcomes.
D) a and b
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference between the new classical theory and the new Keynesian theory is the assumption of
A) rational expectations.
B) adaptive expectations.
C) complete flexibility of wages and prices in the short run.
D) a and c
E) b and c
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-2
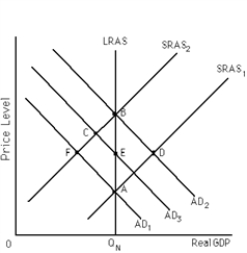 -Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts at point B. Fed monetary policy shifts the AD curve to AD1. A recession is likely if the economy operates under __________ assumptions, which include wage and price __________.
-Refer to Exhibit 16-2. Suppose the economy starts at point B. Fed monetary policy shifts the AD curve to AD1. A recession is likely if the economy operates under __________ assumptions, which include wage and price __________.
A) new classical; flexibility
B) new classical; inflexibilities
C) new Keynesian; flexibility
D) new Keynesian; inflexibilities
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Implied in new Keynesian theory is that when policy is correctly anticipated, there is a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment in
A) neither the short run nor the long run.
B) both the short run and the long run.
C) the short run, but not in the long run.
D) the long run, but not in the short run.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Stagflation
A) is highly unlikely if the Phillips curve is downward sloping.
B) implies that a tradeoff between inflation and unemployment may not always exist.
C) is the simultaneous occurrence of high rates of inflation and unemployment.
D) b and c
E) a, b, and c
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Implicit in the new Keynesian theory is that individuals form their expectations adaptively.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In their 1960 article, Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow found
A) a direct relationship between inflation and investment expenditures.
B) an inverse relationship between inflation and investment expenditures.
C) a direct relationship between inflation and unemployment.
D) an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Samuelson and Solow Phillips curve suggested a(n) __________ relationship between the rate of change in __________ and the unemployment rate.
A) direct; real wage rates
B) inverse; money wage rates
C) inverse; prices
D) direct; prices
E) none of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-6
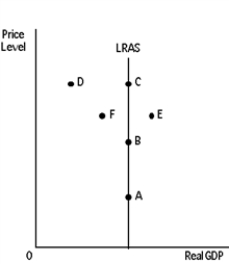 -Refer to Exhibit 16-6. The economy is initially in long-run equilibrium at point A. There is a correctly anticipated increase in aggregate demand, prices and wages are flexible, the economy is self-regulating, and people hold rational expectations. The economy will move to point
-Refer to Exhibit 16-6. The economy is initially in long-run equilibrium at point A. There is a correctly anticipated increase in aggregate demand, prices and wages are flexible, the economy is self-regulating, and people hold rational expectations. The economy will move to point
A) F.
B) C.
C) B.
D) B or C.
E) This exhibit does not show the point the economy would move to.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Milton Friedman argued that as long as
A) the unemployment rate is higher than the inflation rate, the economy is not in long-run equilibrium.
B) Real GDP grows, the inflation rate will fall.
C) the expected inflation rate is not equal to the actual inflation rate, the economy is not in long-run equilibrium.
D) nominal wages rise, so do real wages.
E) none of the above
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The economy is in long-run equilibrium when there is a correctly anticipated increase in aggregate demand. According to new classical theory, the price level will __________ and Real GDP will __________.
A) fall; rise
B) rise; fall
C) fall; remain unchanged
D) rise; remain unchanged
E) remain unchanged; remain unchanged
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The original (1958) Phillips curve stated that
A) unemployment and money wage rates move in the same direction.
B) unemployment and money wage rates move in opposite directions.
C) there is an inverse relationship between price inflation and unemployment.
D) there is a direct relationship between price inflation and unemployment.
E) a and c
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When everyone correctly anticipates that the Fed will buy government securities, then they know that prices will increase. Which of the following adjustments is not likely to occur?
A) Workers will negotiate higher wages.
B) Suppliers of resources will demand higher prices for their resources.
C) Producers will prevent the price level from increasing and hurting their sales.
D) Producers will raise prices.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 16-10
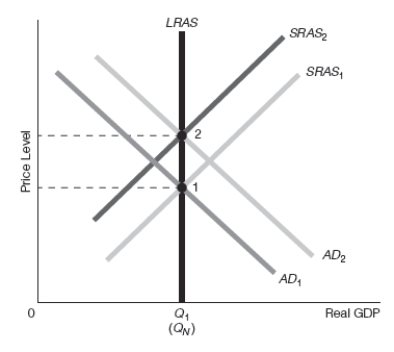 -Refer to Exhibit 16-10. Assume that the starting point is point 1. Suppose that the government implements expansionary fiscal policy that raises aggregate demand. Which of the following best goes with the diagram shown?
-Refer to Exhibit 16-10. Assume that the starting point is point 1. Suppose that the government implements expansionary fiscal policy that raises aggregate demand. Which of the following best goes with the diagram shown?
A) New classical theory with policy incorrectly anticipated, bias downward
B) New classical theory with policy incorrectly anticipated, bias upward
C) Real business cycle theory
D) New classical theory with policy unanticipated
E) Policy ineffectiveness proposition (PIP)
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to a new Keynesian theorist, a correctly anticipated increase in aggregate demand will
A) cause the price level to increase by a greater amount in the short run than what a new classical rational expectations theorist would predict.
B) cause the price level to increase by a smaller amount in the short run than what a new classical rational expectations theorist would predict.
C) cause the price level to increase by the same amount in the short run that a new classical rational expectations theorist would predict.
D) leave the price level unchanged in the short run, but Real GDP will increase more than what a new classical theorist would predict.
E) leave the price level unchanged in the short run, but Real GDP will increase less than what a new classical theorist would predict.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 150
Related Exams