A) the robot used to help produce your car.
B) a computer used by your professor to write this exam.
C) the factory that produces the costume jewelry you buy.
D) the inventory of unsold goods at your local hardware store.
E) an uncut diamond that you discover in your backyard.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An upward-sloping line or curve is used to illustrate:
A) a direct relationship.
B) an inverse relationship.
C) two unrelated variables.
D) the ceteris paribus assumption.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The graph of a direct relationship will have a positive slope.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following pairs is the most likely to exhibit a direct relationship?
A) The price of gasoline and the amount of gasoline that people purchase.
B) Cholesterol levels and the likelihood of developing heart disease.
C) Outdoor temperature and heating oil sales.
D) Annual income and weekly pawn shop visits.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 1A-7 Straight line relationship 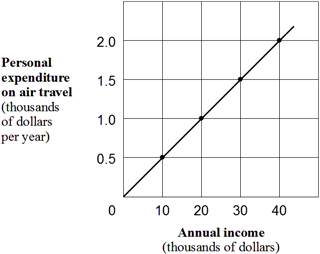 According to Exhibit 1A-7, the relationship between annual income and air-travel expenditures is:
According to Exhibit 1A-7, the relationship between annual income and air-travel expenditures is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) complex.
D) independent.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Computer programs or software are an example of:
A) land.
B) labor.
C) capital.
D) none of the above.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sun is an example of:
A) a natural resource.
B) capital.
C) labor.
D) none of the above.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When economists say scarcity, they mean:
A) there are only a limited number of consumers who would be interested in purchasing goods.
B) the human desire for goods exceeds the available supply of time, goods and resources.
C) most people in poorer countries do not have enough goods.
D) goods are so expensive that only the rich can afford it.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The creative ability of persons to combine and direct resources to produce new products is known as:
A) economizing.
B) entrepreneurship.
C) value judgment.
D) product sensitivity.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Your scarcity problem would disappear if you were rich.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Economists use ____ economic analysis to understand an individual market. They then use ____ economic analysis to guide future national economic policy.
A) b and d
B) macro; micro
C) positive; normative
D) normative; positive
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economics textbook is an example of:
A) capital.
B) labor.
C) a natural resource.
D) entrepreneurship.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a graphic relationship, shifts in a curve are caused by a change in:
A) the slope of the curve.
B) a factor not measured on the axes of the graph.
C) one of the factors measured on either axes of the graph.
D) any factor, whether measured on the axes of the graph of not.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 1A-3 Straight line 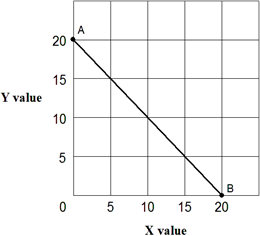 Straight line AB in Exhibit 1A-3 shows that:
Straight line AB in Exhibit 1A-3 shows that:
A) increasing values for X reduces the value of Y.
B) decreasing values for X increases the value of Y.
C) there is an inverse relationship between X and Y.
D) all of the above.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The basic purpose of economic models is to:
A) construct simplifying assumptions about the real world.
B) explain reality in all its complexity.
C) construct situations where controlled experiments can be carried out.
D) provide explanations for, and predictions of the relationship between variables.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An economic model is:
A) a plastic scaled version of the economy.
B) a complete depiction of reality.
C) an abstraction from reality.
D) applicable to consumer behavior but not to producer behavior.
E) not an accepted tool of the economics profession.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the best example of a microeconomic topic?
A) The impact that the money supply has on inflation.
B) The reasons for increases in the price of soft drinks.
C) The effect that federal budget deficits have on the interest rate.
D) The tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To be valid, an economic model must:
A) include every activity which occurs in the real world.
B) include at least 85 percent of the activity which occurs in the real world.
C) be able to predict events occurring in the real world.
D) exclude any link to the real world.
E) not be based on an abstraction of the real world.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A positive economic statement is:
A) an opinion of an action that should be taken.
B) an action that will have a positive effect on the economy.
C) a statement testable by facts.
D) a claim that the speaker is positive will occur.
E) always a microeconomic position.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Macroeconomics deals with the analysis of all of the following questions except:
A) why do national economies grow.
B) what determines a nation's savings and investments.
C) how does a central bank influence inflation.
D) why does a country experience recessions.
E) how does Microsoft price its software packages.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 254
Related Exams