A) Atorvastatin
B) Gemfibrozil
C) Hydrochlorothiazide
D) Losartan
E) Metformin
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 21-year-old health care worker with a history of bulimia nervosa is brought to the hospital due to generalized weakness and dizziness. She reports no vomiting or laxative use. On admission, she is fully responsive. Blood pressure is 110/60 mm Hg and pulse is 102/min. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes. Urine screening for diuretics reveals a large amount of furosemide. Which of the following sets of laboratory findings would most likely suggest that this patient is abusing furosemide to lose weight?
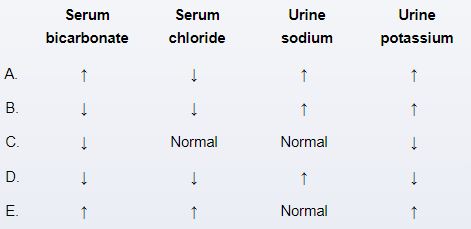
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 62-year-old woman is being evaluated for worsening anemia. The patient was admitted to the hospital 2 days ago due to acute pyelonephritis. She has been treated with intravenous ceftriaxone, and her fever and urinary symptoms have gradually improved. The patient has no history of anemia and has had no symptoms of urinary or gastrointestinal bleeding. Laboratory results are as follows:  Her antibiotics are changed to a different medication class, and the patient is discharged a few days later. At a follow-up office visit 2 weeks later, her laboratory abnormalities have resolved. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anemia?
Her antibiotics are changed to a different medication class, and the patient is discharged a few days later. At a follow-up office visit 2 weeks later, her laboratory abnormalities have resolved. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anemia?
A) Antibody-mediated erythrocyte injury
B) Cytokine-mediated iron dysregulation
C) Drug-induced myelosuppression
D) Erythrocyte enzyme deficiency
E) Microthrombi-induced erythrocyte injury
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 52-year-old man comes to the emergency department (ED) due to 2 hours of burning substernal pain. Before coming to the ED, he took several tablets of antacid at home without any relief. The patient's other medical problems include hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His temperature is 36.7 C (98 F) , blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, and pulse is 92/min. Cardiovascular examination shows normal S1 and S2 without any murmurs. There is no abdominal tenderness. ECG shows ST-segment depression in leads II, III, and aVF. Troponin is 0.06 ng/mL (normal <0.01 ng/mL) . As part of this patient's treatment, enoxaparin therapy is initiated. This drug is expected to bind to which of the following substances in this patient's blood?
A) Antithrombin III
B) Fibrin
C) Plasminogen
D) Protein C
E) Prothrombin
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 31-year-old man comes to the emergency department with a 2-week history of fever, night sweats, and productive cough. He has also had a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. He has no other medical problems. The patient is a software engineer who moved to the United States from Uzbekistan 15 years ago. He takes no medications and has no known drug allergies. His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F) , blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 18/min. He weighs 60 kg (132.3 lb) . Pulse oximetry shows 94% on room air. Chest-x ray reveals a cavitary lesion on the right. Sputum culture is obtained. When exposed to drug A, isolates of the pathogen growing in culture quickly become less resistant to decoloration with an acid-alcohol agent and stop proliferating. Which of the following is drug A most likely to be?
A) Ciprofloxacin
B) Isoniazid
C) Rifampin
D) Streptomycin
E) Vancomycin
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 30-year-old woman is evaluated for almost daily headaches and intermittent blurry vision. Medical history includes obesity but no other chronic conditions. Physical examination shows bilateral symmetric papilledema. There are no other focal neurological deficits. Brain imaging is normal, and blood cell counts and serum chemistry studies are within normal limits. Lumbar puncture reveals elevated opening pressure, and idiopathic intracranial hypertension is diagnosed. Weight loss is advised, and the patient is prescribed acetazolamide therapy. Which of the following changes are most likely to occur in this patient over the next several days due to the medication?
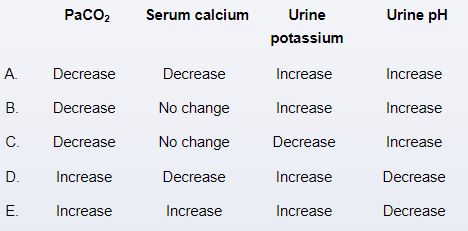
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 22-year-old college student seeks treatment for depressed mood, low energy, poor concentration, and feelings of worthlessness and guilt following a breakup with her partner of 2 years. She is diagnosed with major depression and treated with bupropion and psychotherapy. After 3 weeks of treatment, the patient reports that her energy and motivation have improved somewhat. Her grades, which had been deteriorating, have stabilized. The patient is also continuing to receive psychotherapy and believes that it is beneficial. However, she still feels "really down" at times and has a poor appetite. Further history suggests that the patient consumes very little food each day (a pattern that preceded her use of bupropion) and exercises excessively. Due to her ongoing mood problems, increasing the dose of her antidepressant medication is considered. Which of the following potential side effects of the increased dose would be of primary concern?
A) Agranulocytosis
B) Hypertension
C) Seizures
D) Sexual dysfunction
E) Stevens-Johnson syndrome
F) Weight gain
H) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 44-year-old man reports exertional shortness of breath and palpitations. On examination, he has a systolic murmur at the left sternal border and cardiac apex, which gets louder when he stands up. He is diagnosed with obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, and is started on a medication. Changes in the action potential of ventricular muscle cells before and after administration of medication are shown in the image below  Black curve = Before administration of medication
Red curve = After administration of medicationThe patient is most likely being treated with which of the following medications?
Black curve = Before administration of medication
Red curve = After administration of medicationThe patient is most likely being treated with which of the following medications?
A) Adenosine
B) Digoxin
C) Diltiazem
D) Disopyramide
E) Flecainide
F) Lidocaine
G) Propranolol
I) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 43-year-old woman comes to the office due to occasional chest discomfort over the past year. She describes the pain as a midline pressure or squeezing sensation that lasts 10-15 minutes and is sometimes accompanied by sweating. The patient has no history of hypertension or diabetes mellitus but is a smoker. Ambulatory ECG monitoring shows transient ST-segment elevations in the anteroseptal leads during an episode of chest pain at night. Coronary angiography reveals no atherosclerotic stenosis, but the administration of acetylcholine elicits similar chest pain and ECG changes. Which of the following best explains the coronary intervention findings in this patient?
A) Decreased systemic resistance
B) Endothelial dysfunction
C) Increased venous return
D) Positive inotropic effect
E) Reflex tachycardia
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 29-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the office due to a 2-month history of worsening bilateral nipple discharge that stains her bra. The patient has felt no breast mass and has had no breast pain, headaches, or vision changes. Her last menstrual period was 3 months ago, and home pregnancy tests have been negative. Previously, she had regular menstrual cycles at 28-day intervals. The patient has no other medical conditions and takes no medications. Vital signs are within normal limits. On physical examination, visual fields are intact by confrontation. A whitish fluid can be expressed bilaterally on nipple compression. There are no breast masses or lymphadenopathy. Pelvic examination reveals no abnormalities. Serum beta-hCG testing is negative. Brain imaging shows a 0.6-cm pituitary mass. Pharmacotherapeutic treatment is begun, and on a follow-up visit the patient reports that her symptoms are improving. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of action of this medication?
A) Increased estrogen effect on the pituitary
B) Inhibition of gonadotropin-releasing hormone secretion
C) Inhibition of hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons
D) Stimulation of pituitary dopamine receptors
E) Stimulation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 22-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to fever and a sore throat. Her medical history is significant for Graves disease, for which she recently began taking an antithyroid medication. The patient has no other medical conditions and does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She works as a teacher at an elementary school. Temperature is 38.9 C (102 F) , blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 90/min. Physical examination shows an erythematous pharynx and a normal-sized thyroid. There is no tremor of the outstretched hands. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
A) Acute adrenal insufficiency
B) Drug-induced granulocyte destruction
C) Excessive thyroid suppression
D) Thyroid hormone-induced severe hypermetabolism
E) Viral destruction of neutrophils
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 27-year-old nursing assistant with a history of major depression and bulimia is brought to the emergency department after a suicide attempt. She claims to have ingested several diuretic pills 18 hours ago. The patient complains of frequent, large-volume urinations that started shortly after she ingested the pills. She has also been very thirsty but she denies nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea. Her temperature is 36.7 C (98 F) , blood pressure is 96/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows dry oral mucosa and reduced skin turgor. Laboratory results are as follows:  Which of the following medications did this patient most likely ingest?
Which of the following medications did this patient most likely ingest?
A) Acetazolamide
B) Amiloride
C) Hydrochlorothiazide
D) Spironolactone
E) Torsemide
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 27-year-old woman comes to the office due to severe, unilateral, throbbing headaches that occur several times a month. The headaches are associated with photophobia, nausea, and occasional vomiting. Over-the-counter analgesics do not provide significant symptom relief. Her mother has a history of similar headaches. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination reveals no abnormalities. A medication is prescribed to treat her condition and the patient is instructed to take it immediately at the onset of a headache. This medication most likely decreases the severity and duration of this patient's headache through which of the following mechanisms?
A) Blockade of dopamine receptors in mesolimbic tract
B) Blockade of serotonin reuptake in cortico-amygdala circuitry
C) Increased availability of acetylcholine in cortical synapses
D) Stimulation of periaqueductal gray area mu receptors
E) Stimulation of trigeminovascular serotonin receptors
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 62-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to right upper extremity weakness. Thirty minutes ago, the patient was at his office when he developed difficulty holding a pen. His grip in the right hand was weak and he could not lift his right arm. He tried calling his coworker but could not speak. The patient has never had similar symptoms before. He had no loss of consciousness, weakness of other extremities, vision abnormality, or headache. The symptoms resolved spontaneously by the time paramedics arrived. Medical history is significant for hypertension and a 30-pack-year smoking history. The patient is a defense attorney and recently took on a high-profile case. Temperature is 36.9 C (98.4 F) , blood pressure is 140/84 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min and regular, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows no extremity weakness or sensory loss. There is a left carotid bruit; the remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Noncontrast CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following pharmacotherapies is most appropriate in management of this patient?
A) CNS-targeted immunomodulator
B) GABA A receptor modulator
C) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor
D) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
E) Tissue plasminogen activator
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 32-year-old man comes to the clinic for follow-up due to Crohn disease. The patient was initially diagnosed 3 years ago and achieved disease remission following a course of high-dose glucocorticoids. He remained in remission until 2 months ago, when he experienced an acute flare of diarrhea and abdominal pain that required a brief hospitalization and another course of high-dose glucocorticoids. The patient completed a prescribed glucocorticoid taper earlier this week and says that his symptoms have returned to "about normal." Azathioprine maintenance therapy is started to help prevent future flares. Which of the following most accurately describes the expected effects of this new medication on immune function?
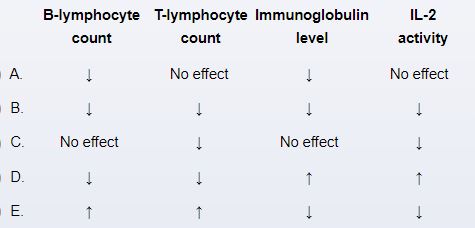
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 48-year-old man comes to the office due to concern that his skin is excessively dry, red, and cracked. The patient explains that he washes his hands each time he touches something due to fear of contamination. He spends 3-4 hours a day washing his hands and showers multiple times daily. He was recently fired from his job after refusing to touch keyboards shared by coworkers and is worried that he will be unable to find employment. On physical examination, the palms are erythematous with peeling skin. Treatment of this patient's disorder is most likely to involve a medication affecting which of the following neurotransmitters?
A) Acetylcholine
B) Dopamine
C) Gamma-aminobutyric acid
D) Glutamate
E) Glycine
F) Histamine
G) Norepinephrine
H) Serotonin
J) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 55-year-old woman is diagnosed with breast cancer and undergoes breast-sparing mastectomy. The tumor margin did not show any invasion, and sentinel axillary lymph node biopsy was negative for nodal metastasis. The tumor was estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor positive but HER-2 negative. After discussion of management options, the patient is started on tamoxifen. While on this medication, she experiences hot flashes that come and go in waves and affect her sleep significantly. Which of the following conditions is the patient also likely to experience as a result of this therapy?
A) Decrease in bone mass
B) Decrease in HDL level
C) Endometrial hyperplasia
D) Fibroadenoma of the breast
E) Increase in LDL level
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 32-year-old man with HIV is diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and started on a 4-drug combination therapy. On a follow-up visit 3 weeks later, he reports red urine and red staining of his contact lenses. A drug susceptibility test of his sputum isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis shows resistance to several antimycobacterial agents. Which of the following best explains the bacterial resistance to the drug responsible for this patient's current symptoms?
A) Altered structure of enzymes involved in bacterial DNA winding-unwinding
B) Altered structure of enzymes involved in bacterial RNA synthesis
C) Altered structure of bacterial ribosomal proteins
D) Decreased activity of bacterial catalase-peroxidase
E) Upregulation of bacterial beta-lactamase synthesis
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 54-year-old man comes to the office due to severe foot pain. The patient attended a wedding reception where he drank several alcoholic beverages, then woke the following morning with pain. He has a long history of gouty arthritis, and his current symptoms are similar to previous flares of the disease. Past medical history includes type 2 diabetes mellitus and recently diagnosed peptic ulcer disease. Physical examination shows erythema, warmth, and swelling at the left first metatarsophalangeal joint. The patient is started on a new medication for gout that provides significant relief of his symptoms, but he returns to the clinic a week later with diarrhea and persistent nausea. The drug used in this patient most likely affects which of the following cell structures?
A) Cytoskeleton
B) Golgi apparatus
C) Microsomes
D) Nucleus
E) Peroxisomes
F) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
G) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
I) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 52-year-old man comes to the office due to easy bruisibility and muscle weakness. Medical history is unremarkable, but the patient has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. Blood pressure is 160/110 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. BMI is 29 kg/m2. Physical examination shows facial plethora, slight centripetal distribution of body fat, diffuse skin pigmentation, and bilateral peripheral edema. Fasting blood glucose is 160 mg/dL and creatinine is 1.2 mg/dL. Chest x-ray reveals a lung mass. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's elevated blood pressure?
A) Activation of renal mineralocorticoid receptors
B) Elevated plasma catecholamine level
C) Impaired glomerular filtration of sodium and water
D) Marked urinary loss of albumin
E) Renal resistance to antidiuretic hormone
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 461 - 480 of 538
Related Exams