A) The energy content of an organism is constant.
B) The organism ultimately must obtain all of the necessary energy for life from its environment.
C) The entropy of an organism decreases with time as the organism grows in complexity.
D) Organisms grow by converting energy into organic matter.
E) Life does not obey the first law of thermodynamics.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a laboratory experiment,you discover that an enzyme-catalyzed reaction has a ∆G of -20 kcal/mol.If you double the amount of enzyme in the reaction,what will be the ∆G for the new reaction?
A) -40 kcal/mol
B) -20 kcal/mol
C) 0 kcal/mol
D) +20 kcal/mol
E) +40 kcal/mol
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements describes enzyme cooperativity?
A) A multienzyme complex contains all the enzymes of a metabolic pathway.
B) A product of a pathway serves as a competitive inhibitor of an early enzyme in the pathway.
C) A substrate molecule bound to an active site of one subunit promotes substrate binding to the active site of other subunits.
D) Several substrate molecules can be catalyzed by the same enzyme.
E) A substrate binds to an active site and inhibits cooperation between enzymes in a pathway.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme is added to a solution where its substrate and product are in equilibrium,what will occur?
A) Additional product will be formed.
B) Additional substrate will be formed.
C) The reaction will change from endergonic to exergonic.
D) The free energy of the system will change.
E) Nothing; the reaction will stay at equilibrium.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some of the drugs used to treat HIV patients are competitive inhibitors of the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme.Unfortunately,the high mutation rate of HIV means that the virus rapidly acquires mutations with amino acid changes that make it resistant to these competitive inhibitors.Where in the reverse transcriptase enzyme would such amino acid changes most likely occur in drug-resistant viruses?
A) in or near the active site
B) at an allosteric site
C) at a cofactor binding site
D) in regions of the protein that determine packaging into the virus capsid
E) Such mutations could occur anywhere with equal probability.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most accurate definition of metabolism for an organism?
A) all chemical reactions
B) all chemical reactions that break down larger molecules into smaller molecules
C) all chemical reactions that take small molecules and condense them into larger molecules
D) all chemical reactions that lead to the production of ATP
E) all chemical reactions that increase the potential energy of the organism
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most similar in structure to ATP?
A) a pentose sugar
B) a DNA nucleotide
C) an RNA nucleotide
D) an amino acid with three phosphate groups attached
E) a phospholipid
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kind of process is digestion?
A) anabolism
B) catabolism
C) inorganic
D) non-energetic
E) organismal
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of metabolism in its entirety in all organisms?
A) Metabolism depends on a constant supply of energy from food.
B) Metabolism depends on an organism's adequate hydration.
C) Metabolism uses all of an organism's resources.
D) Metabolism consists of all the energy transformation reactions in an organism.
E) Metabolism manages the increase of entropy in an organism.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate,the most effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
A) add more of the enzyme.
B) heat the solution to 90°C.
C) add more substrate.
D) add an allosteric inhibitor.
E) add a noncompetitive inhibitor.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When chemical,transport,or mechanical work is done by an organism,what happens to the heat generated?
A) It is used to power yet more cellular work.
B) It is used to store energy as more ATP.
C) It is used to generate ADP from nucleotide precursors.
D) It is lost to the environment.
E) It is transported to specific organs such as the brain.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When ATP releases some energy,it also releases inorganic phosphate.What purpose does this serve (if any) in the cell?
A) The phosphate is released as an excretory waste.
B) The phosphate can only be used to regenerate more ATP.
C) The phosphate can be added to water and excreted as a liquid.
D) The phosphate may be incorporated into any molecule that contains phosphate.
E) It enters the nucleus to affect gene expression.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a statement of the first law of thermodynamics?
A) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
B) The entropy of the universe is decreasing.
C) The entropy of the universe is constant.
D) Kinetic energy is stored energy that results from the specific arrangement of matter.
E) Energy cannot be transferred or transformed.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the questions below.
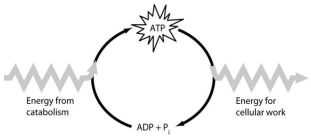 -How do cells use the ATP cycle shown in the figure?
-How do cells use the ATP cycle shown in the figure?
A) Cells use the cycle to recycle ADP and phosphate.
B) Cells use the cycle to recycle energy released by ATP hydrolysis.
C) Cells use the cycle to recycle ADP, phosphate, and the energy released by ATP hydrolysis.
D) Cells use the cycle to generate or consume water molecules as needed.
E) Cells use the cycle primarily to generate heat.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the study of how energy flows through living organisms?
A) metabolism
B) anabolism
C) catabolism
D) bioenergetics
E) thermodynamics
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true when comparing an uncatalyzed reaction to the same reaction with a catalyst?
A) The catalyzed reaction will be slower.
B) The catalyzed reaction will have a different ∆G.
C) The catalyzed reaction will have higher activation energy.
D) The catalyzed reaction will consume all of the catalyst.
E) The catalyzed reaction will have a lower activation energy.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is (are) true for anabolic pathways?
A) They do not depend on enzymes.
B) They are usually highly spontaneous chemical reactions.
C) They consume energy to build up polymers from monomers.
D) They release energy as they degrade polymers to monomers.
E) They consume energy to decrease the entropy of the organism and its environment.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions are based on the reaction A + B ↔ C + D shown in the figure below.
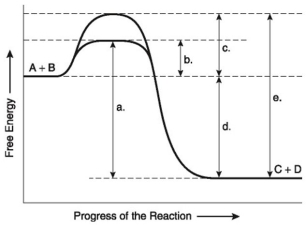 -Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure above?
-Which of the following represents the activation energy required for a noncatalyzed reaction in the figure above?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Zinc,an essential trace element for most organisms,is present in the active site of the enzyme carboxypeptidase.The zinc most likely functions as a(n)
A) competitive inhibitor of the enzyme.
B) noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme.
C) allosteric activator of the enzyme.
D) cofactor necessary for enzyme activity.
E) coenzyme derived from a vitamin.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following figure to answer the question below.
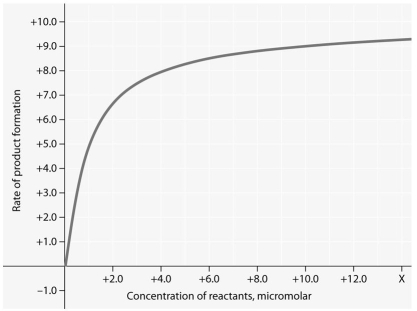 Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
concentration,with the concentration of enzyme constant.
-When is a reaction at chemical equilibrium?
Rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction as a function of varying reactant
concentration,with the concentration of enzyme constant.
-When is a reaction at chemical equilibrium?
A) when the reactants are at the same concentration as the products
B) when the forward and backward reactions occur at the same rate
C) when there is no reactant remaining
D) when there is no product remaining
E) A reaction never reaches chemical equilibrium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 92
Related Exams