A) The protein has been degraded into its amino acids at pH 8.4.
B) The protein has changed shape due to a change in charge.
C) The protonation state of amino acids involved in the catalytic mechanism has changed.
D) B and C above.
E) All of the above.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the following to their functions. -21st amino acid in many species
A) N-formylmethionine
B) Histamine
C) S-adenosylmethionine
D) g-aminobutyrate
E) selenocysteine
F) epinephrine (adrenaline)
H) C) and F)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the net charge on the tripeptide Gly-Arg-Lys at pH 7? The table below gives the pKa's of the ionizable groups on the free amino acids. 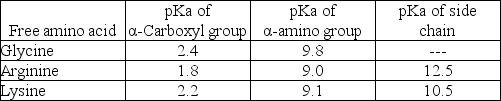
A) -1
B) 0
C) +1
D) +2
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ammonium sulfate is often used as a first step in protein purification because it
A) buffers solutions and protects the protein.
B) precipitates many proteins.
C) precipitates all proteins.
D) hydrolyzes proteins into their constituent amino acids.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proline is distinct among the 20 commonly found amino acids because
A) it is a ring compound.
B) it is hydrophilic and ionic.
C) the nitrogen of the amino group is in a ring.
D) the carbon of the carboxyl group is in a ring.
E) it has little effect on protein structure.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Amino acids and amino acid derivatives can be used to modify proteins.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two proteins are determined to have descended from a common ancestor they are
A) heterogeneous.
B) amphipathic.
C) taxolinked.
D) homologous.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cation-exchange resins have negatively charged groups covalently attached to the column matrix.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The liquid that emerges from the bottom of a chromatographic column is called the supernatant.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cystine is likely to be isolated from proteins that are
A) high in methionine.
B) in the cell nucleus.
C) intracellular.
D) extracellular.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the purpose of SDS in SDS-PAGE?
A) To selectively bind the target protein.
B) To maintain buffer pH in the gel.
C) To cause the separation to be on the basis of molecular weight only.
D) To initiate polymerization of acrylamide to form a gel.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary structure of a protein specifically describes the ________.
A) location of disulfide bonds
B) linear sequence of amino acids
C) overall three-dimensional shape
D) Φ and Ψ angles for each amino acid
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sequence of amino acids with a relatively high hydropathy is very likely to function by
A) being at the active site of an enzyme.
B) being embedded in a cell membrane.
C) making a protein soluble.
D) being on the protein surface.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the amino acid lysine,the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be applied to ________ ionization group(s) .
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pKa's of arginine's α-Carboxyl group,α-Amino group and side chain are 1.8,9.0 and 12.5,respectively.Calculate the isoelectric point.
A) 7.8
B) 7.2
C) 10.8
D) 5.4
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The isoelectric point of alanine is pH = 6.15.It is mixed with proline (pHCOOH = 2.0;pHNH₂ = 10.6) ,and the mixture is placed in an electric field at pH 6.15.Which statement is true?
A) The two amino acids will be separated.
B) The two amino acids will not be separated.
C) Neither amino acid will move in the electric field.
D) Both amino acids will move from the origin and be separated.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which technique is used less for protein purification and more for the determination of molecular weights?
A) Affinity chromatography.
B) SDS-PAGE.
C) Gel filtration.
D) Ion exchange chromatography.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the R group of an amino acid is -CH₃,then the name of this compound is
A) methyl amino acid.
B) 2-aminopropanoic acid.
C) alanine.
D) All of the above.
E) B and C.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The overall shape of a protein is greatly influenced by
A) amino acid R group properties.
B) charged amino acids.
C) hydrophobic amino acids.
D) pH.
E) hydrophilic amino acids.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Amino acids with non-ionizable side chains are zwitterions when they are ________.
A) in any solution
B) at physiological pH,pH = 7.4
C) in acidic solutions only
D) in alkaline solutions only
E) All of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 107
Related Exams