A) P* and Q* to climb.
B) P* to climb while Q* falls.
C) P* to climb while Q* holds steady.
D) P* to fall while Q* climbs.
E) P* and Q* to fall.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If you observe a stationary price for some commodity, you can guess that demand and supply curves intersect at that price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a competitive market, price is determined by:
A) the costs of producing the good in question.
B) the supply of the good.
C) the decisions of the buyers about how much they are willing to pay.
D) the interaction of tastes and demand.
E) all of the above.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An increase in price will lead to a lower quantity demanded because:
A) suppliers will supply only the smaller amount.
B) some individuals will no longer purchase the good.
C) individuals purchase less of the good.
D) a and b.
E) b and c.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One reason that supply curves display positive slope is that:
A) expanded production may require the use of superior resources.
B) people are not willing to pay a higher price for more goods.
C) expanded industry output might cause a labor shortage and subsequently increase the wage rate included in the cost of production.
D) extra production brings in the more efficient, lower-cost producers.
E) the law of diminishing returns is important to producers.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
When a big movement of hogs to market causes pork prices to fall, this will tend to push beef prices down also.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the law of demand:
A) the intersection of demand and supply establishes the market equilibrium point.
B) consumers' tastes can influence the quantity demanded.
C) there is an inverse relationship between price and the quantity demanded.
D) "all other things held equal" is an important concept.
E) there is a direct relationship between price and the quantity demanded.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in demand means a movement to a higher price along a given demand curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Equilibrium occurs where the demand curve intersects the supply curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given a fixed supply of lamb chops, a reduction in the price of pork chops (close substitutes) will tend to:
A) shift the demand curve for lamb chops to the right.
B) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the right.
C) shift the demand curve for pork chops to the left.
D) raise the price of lamb chops.
E) lower the price of lamb chops.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume that the demand for penicillin as reflected in the figure below is P = 40 - .1Q, while supply is P = 10 + .9Q.Market equilibrium would be given by: 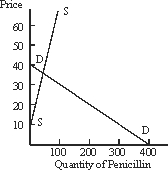
A) P = 37, Q = 30
B) P = 30, Q = 37
C) P = 40, Q = 36
D) P = 370, Q = 30
E) None of the above
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One reason why the quantity demanded of a good tends to fall as its price rises is that:
A) the increase in price shifts the supply curve upward.
B) the increase in price shifts the demand curve downward.
C) at higher prices, suppliers are willing to supply less.
D) people feel poorer and cut down on their use of the good.
E) demand has to fall to restore equilibrium after a price rise.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Upward-sloping supply curves are the result of:
A) increasing returns to scale.
B) increasing costs of labor.
C) changes in government policies.
D) changes in technology.
E) none of the above
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure 3-3 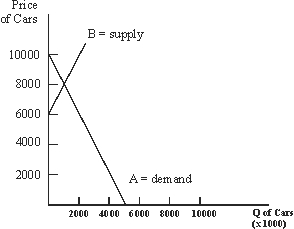 -Assume that automotive workers go on strike, so that the production of cars falls.Given the supply and demand curves in Figure 3-3, which of the following would result in comparison to the initial equilibrium position?
-Assume that automotive workers go on strike, so that the production of cars falls.Given the supply and demand curves in Figure 3-3, which of the following would result in comparison to the initial equilibrium position?
A) Prices fall, Quantity falls
B) Prices rise, Quantity falls
C) Prices rise, Quantity rises
D) Prices and Quantity do not change.
E) None of the above.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A price at which the amount people wish to buy exceeds the amount that people wish to produce (given upward-sloping supply curves) :
A) lies above the equilibrium, market clearing price.
B) lies below the market clearing price.
C) will induce a shift in the demand schedule to achieve equilibrium.
D) is impossible.
E) is none of the above.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the price of bread is causing quantity demanded to increase but not quantity supplied, the price will begin to be pushed upward.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The high and rising price of lobsters must be indicative of monopoly in the lobster fishing market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Lower prices coax out higher quantities demanded along a downward-sloping demand curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An equilibrium point could conceivably lie on the supply schedule, but not the demand schedule.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions :
Figure 3-1 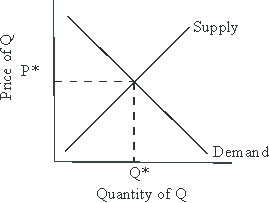 -Let P* and Q* represent market clearing price and quantity, respectively.Given the supply and demand curves drawn in Figure 3-1, the appearance of foreign suppliers willing to sell any quantity at a price slightly higher than equilibrium can be expected to cause:
-Let P* and Q* represent market clearing price and quantity, respectively.Given the supply and demand curves drawn in Figure 3-1, the appearance of foreign suppliers willing to sell any quantity at a price slightly higher than equilibrium can be expected to cause:
A) P* and Q* to climb.
B) P* and Q* to fall.
C) P* to climb while Q* falls.
D) Q* to fall while P* holds steady.
E) none of the above.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 85
Related Exams