A) The catalyst speeds up the attainment of equilibrium.
B) If the reactants are capable of forming many different products,a catalyst may selectively speed up one reaction over another.
C) The catalyst increases the rate of both the forward and the reverse reaction.
D) The catalyst increases the yield of the products.
E) The catalyst is not consumed in either the forward or the reverse reaction.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When cobalt chloride is added to pure water,the Co2+ ions hydrate.The hydrated form then reacts with the Cl- ions to set up the equilibrium shown here:
Co(H2O) 62+ + 4Cl-  CoCl42- + 6H2O
(pink)
(blue)
Which statement accurately describes the change that the system will undergo if water is added?
CoCl42- + 6H2O
(pink)
(blue)
Which statement accurately describes the change that the system will undergo if water is added?
A) The color will become more blue.
B) The equilibrium will shift to the right.
C) More water will be produced.
D) More chloride ions will be produced.
E) There will be less of the hydrated cobalt ion at the new equilibrium position.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Carbon tetrachloride may react with oxygen to produce chlorine and carbonyl chloride.
2CCl4(g) + O2(g)  2COCl2(g) + 2Cl2(g) ; Kc = 9.9 × 1051
What is Kc for the following equilibrium?
COCl2(g) + Cl2(g)
2COCl2(g) + 2Cl2(g) ; Kc = 9.9 × 1051
What is Kc for the following equilibrium?
COCl2(g) + Cl2(g)  CCl4(g) + 1/2O2(g)
CCl4(g) + 1/2O2(g)
A) 9.9 × 10-51
B) 5.0 × 10-53
C) 1.0 × 10-26
D) 1.0 × 10-52
E) -9.9 × 1051
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of ammonia gas was allowed to come to equilibrium at 400 K.
2NH3(g)  N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0372 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0124 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.175 M.What is Kp for this equilibrium? (R = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/(K ∙ mol) )
N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0372 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0124 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.175 M.What is Kp for this equilibrium? (R = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/(K ∙ mol) )
A) 4.28
B) 2.85
C) 1.70 × 10-2
D) 1.95 × 10-8
E) 2.26 × 10-2
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of ammonia gas was allowed to come to equilibrium at 400 K.
2NH3(g)  N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0551 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0183 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.383 M.What is Kc for this equilibrium?
N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0551 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0183 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.383 M.What is Kc for this equilibrium?
A) 3.97 × 10-3
B) 1.58 × 10-5
C) 2.10 × 10-5
D) 2.40 × 10-1
E) 2.65 × 10-3
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sample of ammonia gas was allowed to come to equilibrium at 400 K.
2NH3(g)  N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0484 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0161 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.295 M.What was the initial concentration of ammonia?
N2(g) + 3H2(g)
At equilibrium,it was found that the concentration of H2 was 0.0484 M,the concentration of N2 was 0.0161 M,and the concentration of NH3 was 0.295 M.What was the initial concentration of ammonia?
A) 0.161 M
B) 0.228 M
C) 0.36 M
D) 0.311 M
E) 0.328 M
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following equilibrium is established in a sealed,rigid container.How could the partial pressure of SO2 at equilibrium be increased?
SO2Cl2(g)  SO2(g) + Cl2(g) ; ΔH = +67 kJ
SO2(g) + Cl2(g) ; ΔH = +67 kJ
A) by adding an inert gas such as helium
B) by increasing the temperature
C) by removing SO2Cl2 as it is formed
D) by adding Cl2 to the system
E) by decreasing the volume of the reaction vessel
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the reaction quotient (Q) for the equilibrium
TlSCN(s)  Tl+(aq) + SCN-(aq)
When 0.1837 L of
Tl+(aq) + SCN-(aq)
When 0.1837 L of 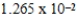 M Tl+ is combined with 0.1335 L of
M Tl+ is combined with 0.1335 L of 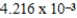 M SCN- in the presence of an excess of TlSCN(s) ?
M SCN- in the presence of an excess of TlSCN(s) ?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following reactions does an instantaneous increase in the volume of the reaction vessel favor formation of the products?
A) PCl5(g) ![]() PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
B) N2(g) + 3H2(g) ![]() 2NH3(g)
2NH3(g)
C) H2(g) + I2(g) ![]() 2HI(g)
2HI(g)
D) MgO(s) + CO2(g) ![]() MgCO3(s)
MgCO3(s)
E) N2(g) + O2(g) ![]() 2NO(g)
2NO(g)
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When cobalt chloride is added to pure water,the Co2+ ions hydrate.The hydrated form then reacts with the Cl- ions to set up the equilibrium shown here:
Co(H2O) 62+ + 4Cl-  CoCl42- + 6H2O
(pink)
(blue)
Which statement describes the change that the system will undergo if potassium chloride is added?
CoCl42- + 6H2O
(pink)
(blue)
Which statement describes the change that the system will undergo if potassium chloride is added?
A) It should become more pink.
B) Nothing will change.
C) The silver ion will react with the CoCl42-.
D) Water will be produced.
E) It should become more blue.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction:
2HF(g)  H2(g) + F2(g) (Kc = 1.00 × 10-2)
Given that 1.00 mol of HF(g) ,0.200 mol of H2(g) ,and 0.750 mol of F2(g) are mixed in a 5.00-L flask,determine the reaction quotient,Q.
H2(g) + F2(g) (Kc = 1.00 × 10-2)
Given that 1.00 mol of HF(g) ,0.200 mol of H2(g) ,and 0.750 mol of F2(g) are mixed in a 5.00-L flask,determine the reaction quotient,Q.
A) Q = 0.0375
B) Q = 0.150
C) Q = 0.0300
D) Q = 1.95
E) none of these
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When gaseous carbon monoxide and hydrogen are combined in a sealed vessel and heated they will eventually form an equilbrium mixture of reactants and products according to the balanced chemical equilibrium below.
CO(g) + 3H2(g)  CH4(g) + H2O(g)
In one such reaction 3 moles of one reactant were combined with 1 mole of the other reactant in a fixed volume vessel and heated to 1200 K.Analysis of the reaction mixture at various times gave the results below.Which component of the reaction mixture is represented by curve B?
CH4(g) + H2O(g)
In one such reaction 3 moles of one reactant were combined with 1 mole of the other reactant in a fixed volume vessel and heated to 1200 K.Analysis of the reaction mixture at various times gave the results below.Which component of the reaction mixture is represented by curve B? 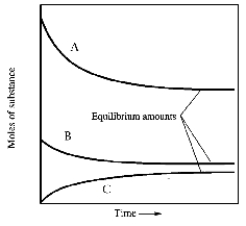
A) carbon monoxide
B) either methane or water
C) hydrogen
D) either hydrogen or carbon monoxide
E) not enough information to decide
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction Br2(g) + Cl2(g)  2BrCl(g) ,at equilibrium,it is found that the concentrations of Br2,Cl2,and BrCl are 0.484 M,0.105 M,and 1.24 × 10-3 M,respectively.What is the value of Kc?
2BrCl(g) ,at equilibrium,it is found that the concentrations of Br2,Cl2,and BrCl are 0.484 M,0.105 M,and 1.24 × 10-3 M,respectively.What is the value of Kc?
A) 3.01 × 10-5
B) 1.20 × 10-4
C) 2.43 × 10-2
D) 4.12 × 101
E) 3.32 × 104
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 35.00-L vessel at 700 K initially contains HI(g) at a pressure of 5.80 atm; at equilibrium,it is found that the partial pressure of H2(g) is 0.56 atm.What is the partial pressure of HI(g) at equilibrium?
2HI(g)  H2(g) + I2(g)
H2(g) + I2(g)
A) 5.8 atm
B) 5.23 atm
C) 4.67 atm
D) 6.36 atm
E) 0.561 atm
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The _____ is an economical process for making nitric acid in which nitric oxide is prepared by the oxidation of ammonia.
A) Hall-Héroult process
B) Ostwald process
C) Frasch process
D) Bessemer process
E) Castner process
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 800 K,Kc for the following equilibrium is 4.2 × 10-3.
2HgO(s)  2Hg(l) + O2(g)
Suppose 82.3 g of mercury (II) oxide is placed in a sealed 2.50-L vessel at 800 K.What is the partial pressure of oxygen gas at equilibrium? (R = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/(K ∙ mol) )
2Hg(l) + O2(g)
Suppose 82.3 g of mercury (II) oxide is placed in a sealed 2.50-L vessel at 800 K.What is the partial pressure of oxygen gas at equilibrium? (R = 0.0821 L ∙ atm/(K ∙ mol) )
A) 8.7 atm
B) 4.3 atm
C) 0.27 atm
D) 0.0042 atm
E) 22 atm
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following reaction system at equilibrium,which one of the changes below would cause the equilibrium to shift to the right?
Br2(g) + 2NO(g)  2NOBr(g) ; ΔH° = -30 kJ
2NOBr(g) ; ΔH° = -30 kJ
A) Remove some NO.
B) Remove some Br2.
C) Add some NOBr.
D) Increase the volume of the reaction vessel.
E) Decrease the temperature.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction 2HI(g)  H2(g) + I2(g) ,Kc = 0.290 at 400 K.If the initial concentrations of HI,H2,and I2 are all 1.50 × 10-3 M at 400 K,which one of the following statements is correct?
H2(g) + I2(g) ,Kc = 0.290 at 400 K.If the initial concentrations of HI,H2,and I2 are all 1.50 × 10-3 M at 400 K,which one of the following statements is correct?
A) The concentrations of HI and I2 will increase as the system is approaching equilibrium.
B) The concentrations of H2 and I2 will increase as the system is approaching equilibrium.
C) The system is at equilibrium.
D) The concentrations of H2 and HI will decrease as the system is approaching equilibrium.
E) The concentration of HI will increase as the system is approaching equilibrium.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the equilibrium PCl5(g)  PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ,Kc = 2.0 × 101 at 240°C.If pure PCl5 is placed in a 1.00-L container and allowed to come to equilibrium,and the equilibrium concentration of PCl3(g) is 0.27 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g) ?
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ,Kc = 2.0 × 101 at 240°C.If pure PCl5 is placed in a 1.00-L container and allowed to come to equilibrium,and the equilibrium concentration of PCl3(g) is 0.27 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g) ?
A) 0.54 M
B) 0.13 M
C) 0.013 M
D) 0.0036 M
E) 8.6 M
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following equilibrium:
CO2(g) + C(graphite)  2CO(g) ; ΔH = 172.5 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction will
2CO(g) ; ΔH = 172.5 kJ
The equilibrium constant for this reaction will
A) increase if the temperature is decreased.
B) decrease with increasing temperature.
C) increase at some pressures and decrease at other pressures.
D) increase with increasing temperature.
E) not change if the temperature is increased.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 97
Related Exams