A) Wait for the economy to fix itself.
B) Use monetary restraint.
C) Get consumers to spend less on goods and services.
D) Get consumers to spend more on goods and services.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the economy has an inflationary GDP gap,one possible solution is to increase government expenditures. Fiscal restraint is tax hikes or spending cuts intended to reduce (shift)aggregate demand.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an income transfer?
A) Free medical care made available to the poor by a private physician.
B) Unemployment benefits paid to a factory worker who was laid off.
C) A new highway built by the federal government.
D) A gift of money from a parent to a chilD.Income transfers are payments to individuals for which no current goods or services are exchanged,such as Social Security,welfare,and unemployment benefits.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
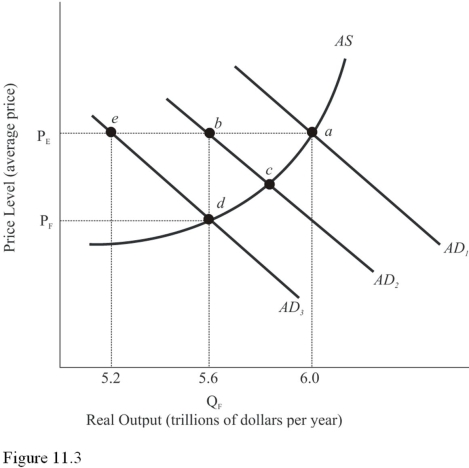 Refer to Figure 11.3.Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $5.6 trillion.If aggregate demand decreases by the amount of the GDP gap,equilibrium will occur at
Refer to Figure 11.3.Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $5.6 trillion.If aggregate demand decreases by the amount of the GDP gap,equilibrium will occur at
A) Point a.
B) Point b.
C) Point c.
D) Point D.Equilibrium occurs where the new aggregate demand AD2 and AS intersect,at point c.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The statement "balancing the budget on the backs of the poor" refers to
A) Transfer payment cuts in order to reduce government expenditures.
B) Tax increases on the poor in order to increase government revenues.
C) Government spending increases in order to increase aggregate expenditures.
D) Government spending cuts on public parks in order to reduce government expenditures.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Prior to 1913,most of the federal government's tax revenues came from
A) Social Security payroll taxes.
B) Customs,whiskey,and tobacco taxes.
C) Individual income taxes.
D) Corporate income taxes.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would not be a policy option to eliminate an AD shortfall?
A) Increase government purchases.
B) Reduce taxes.
C) Reduce transfer payments.
D) Increase transfer payments.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Time lags in the design,authorization,and implementation of fiscal policy reduce its effectiveness. In the time it takes for fiscal policy to take effect,the economy could begin to improve on its own due to other internal or external shocks that may have occurred.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Fiscal policy changes in government spending and taxes primarily target the aggregate supply curve. The federal government's tax and spending powers give it a great deal of influence over aggregate demand.The government can alter aggregate demand by purchasing more or fewer goods and services,raising or lowering taxes,and changing the level of income transfers.These tools primarily impact the aggregate demand,not the aggregate supply.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Payments for unemployment benefits sent to unemployed people are considered government purchases. Income transfers,not government purchases,are payments to individuals for which no current goods or services are exchanged,such as Social Security,welfare,and unemployment benefits.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The recessionary GDP gap will differ from the AD shortfall when the
A) Multiplier effect raises spending.
B) Budget is balanced.
C) Aggregate supply curve slopes upward.
D) Multiplier effect lowers spending.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
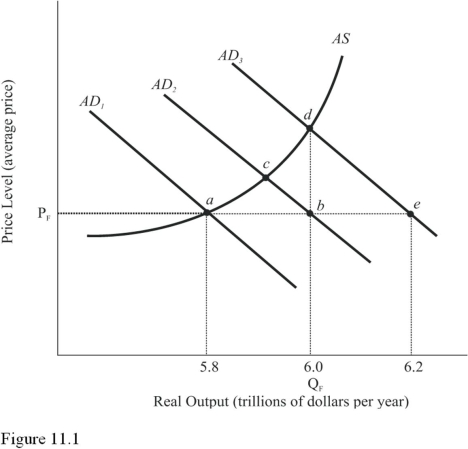 Using Figure 11.1,which fiscal policy action would increase aggregate demand from AD1 to AD3?
Using Figure 11.1,which fiscal policy action would increase aggregate demand from AD1 to AD3?
A) A decrease in transfer payments.
B) A decrease in taxes.
C) A decrease in government spending.
D) A decrease in government spending matched by an equal decrease in taxes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume the MPC is 0.80.If the government wants to eliminate an AD shortfall of $300 billion,it should
A) Cut taxes by $75 billion.
B) Cut taxes by $240 billion.
C) Increase taxes by $60 billion.
D) Cut taxes by $60 billion.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An investment tax credit creates jobs mostly for the year in which it is granted. A tax cut may also be an effective mechanism for increasing investment spending.Once additional investment spending enters the circular flow,it too has a multiplier effect.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the GDP gap is $400 billion and AS is upward-sloping,an effective fiscal policy would be to increase aggregate demand by $400 billion. With an upward-sloping aggregate supply curve,if aggregate demand increased by the amount of the recessionary GDP gap,the economy would fall short of full employment.Some of the increased demand pushes up prices instead of output.To reach full-employment equilibrium,the AD curve must shift by an amount greater than the GDP gap,the amount of the entire AD shortfall.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
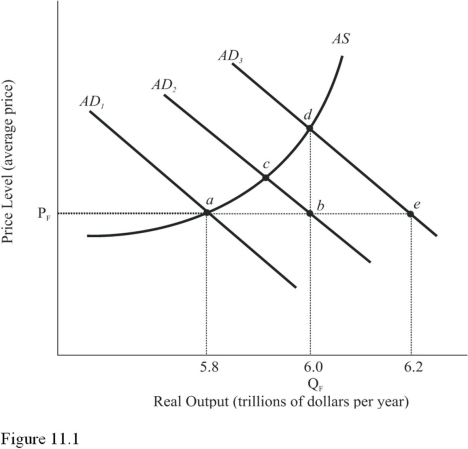 Refer to Figure 11.1.Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion.The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
Refer to Figure 11.1.Assume aggregate demand is represented by AD1 and full-employment output is $6.0 trillion.The economy confronts a real GDP gap of
A) $.2 trillion.
B) $.4 trillion.
C) $.6 trillion.
D) None of the choices are correct.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Fiscal policy formation causes a delay in implementation even though a recession can usually be recognized within a few weeks after it begins. A limitation on fiscal policy is time.In the real world it takes time to recognize that the economy is in trouble.A blip in the unemployment or inflation rate may not signal a trend.Before intervening,we may want to be more certain that a recessionary or inflationary GDP gap is emerging.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a policy option to eliminate an AD shortfall?
A) Decrease government purchases.
B) Reduce taxes.
C) Reduce transfer payments.
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following formulas is used to find the cumulative increase in AD from a particular fiscal stimulus?
A) Fiscal stimulus ÷ the multiplier.
B) Fiscal stimulus ÷ MPC.
C) The multiplier × fiscal stimulus.
D) MPC × fiscal stimulus.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The desired fiscal restraint is equal to
A) Excess AD times the multiplier.
B) Excess AD divided by the multiplier.
C) Desired AD reduction.
D) GDP gap divided by the multiplier.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 153
Related Exams